Subqueries in Oracle divided into 3 categories:
- Single-Row Subquery
- Multi-Row Subquery
- Correlated Subquery
In this article we will go through Single and Multi-Row subqueries. To read about Correlated subquery, click here.
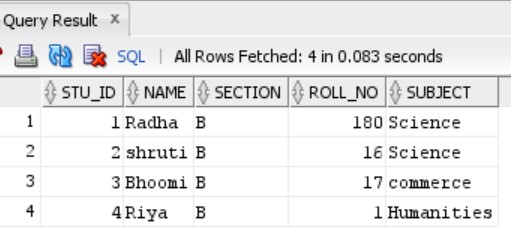
Follow the Stu Table as shown below:
1. Single-Row Subquery
Single Row Subqueries are among those nested queries that return a single row as an output. There is some operators list that can be used before subqueries. =,<,>,<=,>= are those operators.
Example
We want to find out details of those Students that Stu_id more than the Student having Roll number=16 :
Select * from Stu
Where Stu_id>(Select Stu_id from Stu where Roll_No=16);OUTPUT:
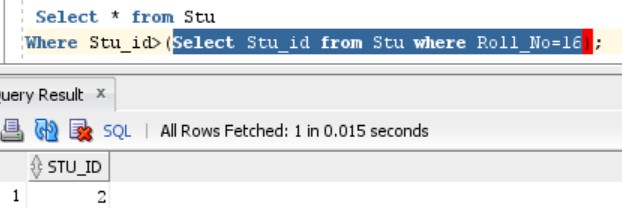
The highlighted part in the output above displays a single-row subquery. The execution of this highlighted query displays the output as above. It can be noticed that the query returns a single row.
2. Multi-Row Subquery
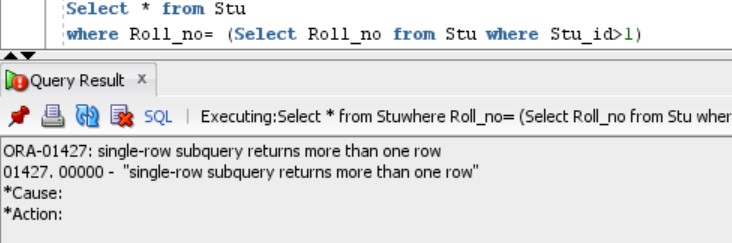
Multi-line Subqueries are amongst those subqueries, that return multiple rows as an output. Now, consider a situation wherein we need the list of those Students who have Roll_no equal to those having Stu_id>1.
Select * from Stu
where Roll_no= (Select Roll_no from Stu where Stu_id>1)But we can see that the above code will display an error and the error mentions:
OUTPUT:
This is because the multiline subquery returns multiple rows as an output. So we need to put a multiline operator preceding the subquery to perform the same task. Some Operators are:
- ANY Operator
- ALL Operator
- IN Operator
- EXIST Operator,
- NOT EXIST Operator,
Example
We want the list of those Students who have Roll_no equal to those having Stu_id>1.
Select * from Stu
where Roll_no= ANY(Select Roll_no from Stu where Stu_id>1)OUTPUT:
The output displays a multiline subquery that is marked as highlighted below. You can see executing the subquery has returned 3 rows.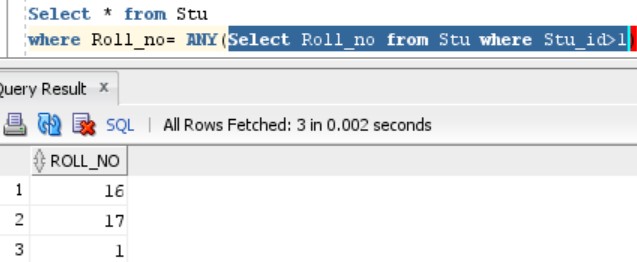
- Log in to post comments