NATURAL JOIN in Oracle is the type of Joins that can easily access two or more tables at a similar time with the common column present in those tables.
Natural Join Syntax in Oracle
SELECT Column from table1 NATURAL JOIN table2;Remember
- The column of the same name must have the same datatype as well.
- It does not exclude duplicate rows.
- In case Natural join does not satisfy data type and same column name condition then it will return the cartesian result.
Oracle Natural Join Example
Suppose we have two tables Stu and details as below:
Stu:
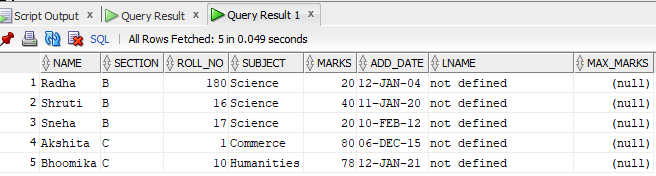
details:
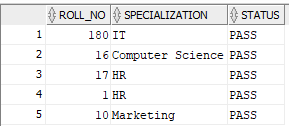
Now, if we want to combine two of the table by a common column Roll_No:
Select * from Stu s, details d
where s.Roll_No = d.Roll_No;Output
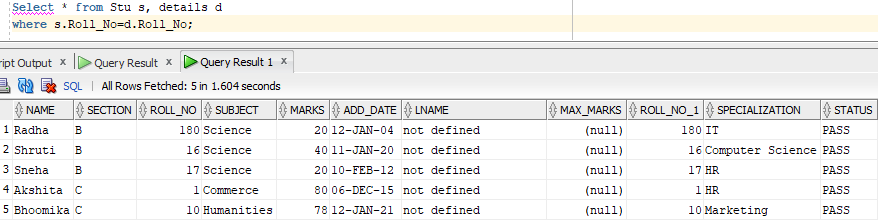
The same can be done using NATURAL JOIN. However, making the syntax much easier.
Now, if we want to perform the same operation using NATURAL JOIN, the code will be as follows:
Select * from Stu NATURAL JOIN details;Output
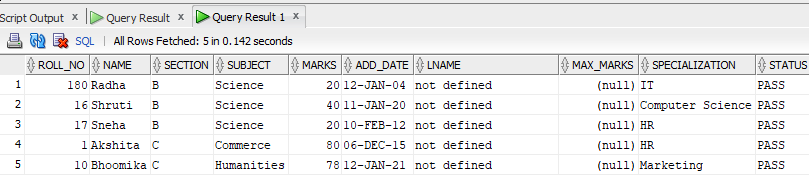
NOTE The only difference you can find here is that the duplicate columns are not allotted to the common column as it was done in the very first example, without using Natural Join.
How many total rows will be there in Output of Natural Join?
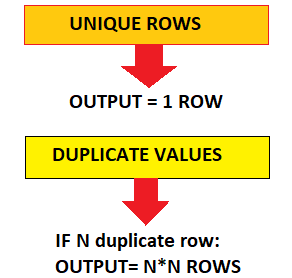
Example
We have the following Stu Table:
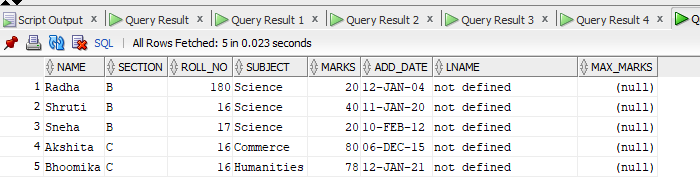
And below is the details table:
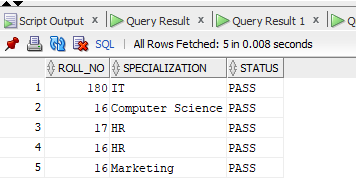
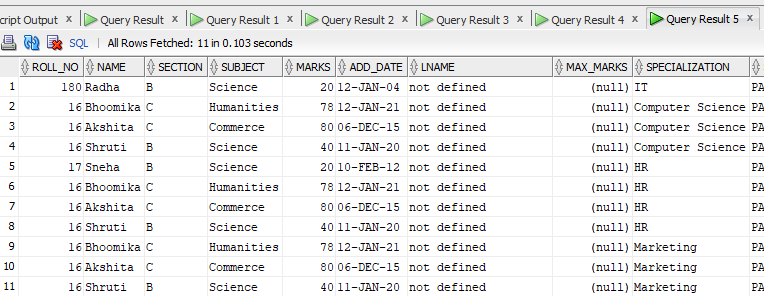
If we want to apply Natural Join to both the Stu and details table, the Output table will contain the following rows:
Unique values= 180 and 17 i.e. 1+1 = 2 Rows
Duplicate Values= 16, 16 and 16 i.e. 3 Duplicate values. So, 3 * 3 = 9 Rows
Total output Rows= 2 + 9 = 11 Rows.
Output
- Log in to post comments