As we have discussed in the previous articles about the SET operators. You can click here to check about SET Operators in Oracle.
Let's move ahead with the case study and solve queries using SET Operator as follows:
QYERY 1:LIST OUT THE DISTINCT JOBS IN SALES AND RESEARCH DEPARTMENTS
Distinct Jobs here means that there should not be any duplication. We will solve this query using the UNION Operator in Oracle.
Select * from job where job_id in (Select job_id from employee
where department_id=(select department_id from department where name='Sales'))
UNION
Select * from job where job_id in (Select job_id from employee
where department_id=(select department_id from department where name='Research'))
Output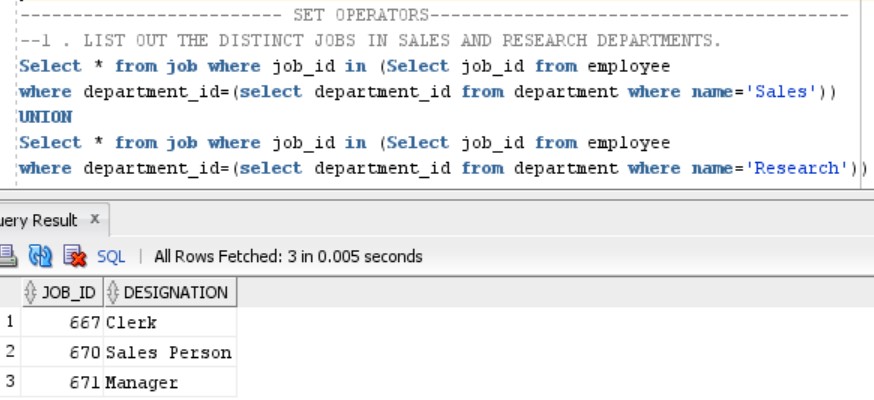
QUERY 2:LIST OUT ALL THE JOBS IN SALES AND RESEARCH DEPARTMENTS
In this we need to list all the jobs present in the Sales and Research Departments. So, here the result can contain duplications too. As same job designations can be present in 2 different departments.
Therefore, we will proceed with this query using UNION ALL Operator in Oracle.
Select * from job where job_id in (Select job_id from employee
where department_id=(select department_id from department where name='Sales'))
UNION ALL
Select * from job where job_id in (Select job_id from employee
where department_id=(select department_id from department where name='Research')) Output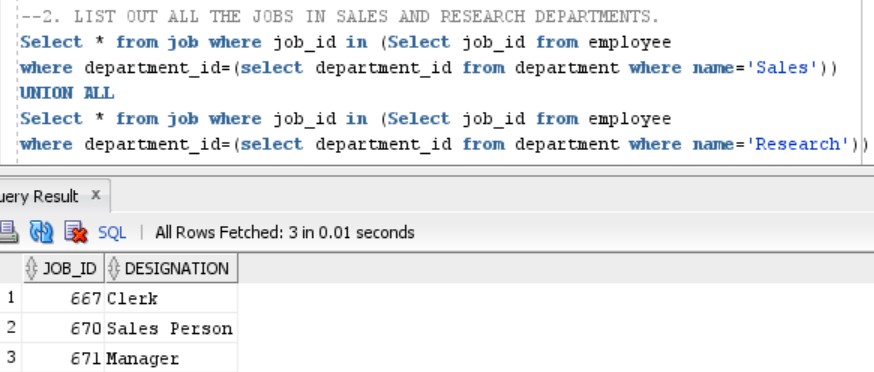
QUERY 3:LIST OUT THE COMMON JOBS IN RESEARCH AND ACCOUNTING DEPARTMENTS IN ASCENDING ORDER
This Query demands to find common Jobs. Hence, we will use INTERSECTION Operator to solve this:
Select designation from job where job_id in (Select job_id from employee
where department_id=(select department_id from department where name='Research'))
INTERSECT
Select designation from job where job_id in (Select job_id from employee
where department_id=(select department_id from department where name='Operation'))
order by designationOutput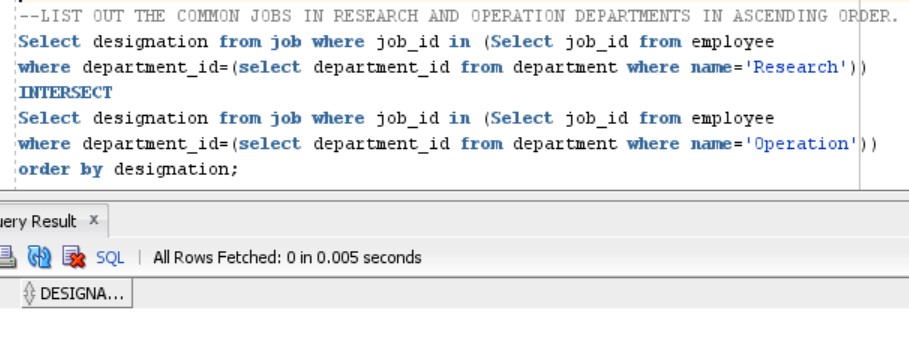
- Log in to post comments