In this article, we will read a text file and print out its content.
Example:
- To represent the text file, create a File object.
- To read the contents of the file, create a Scanner object.
- Use the Scanner object to read the contents of the file line by line or character by character.
- Close the Scanner object to free up its resources.
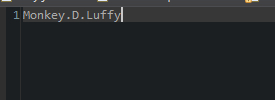
- Here is the text file content.
package week1.day2;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Calculator {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// Create a File object to represent the text file
File file = new File("C:\\Users\\arili\\git\\Assignments\\Selenium\\target\\OnePiece.txt");
try {
// Create a Scanner object to read the contents of the file
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(file);
// Use the Scanner object to read the contents of the file line by line
while (scanner.hasNextLine()) {
String line = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println(line);
}
// Close the Scanner object to release the resources used by it
scanner.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
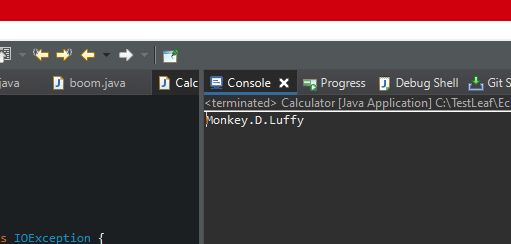
}- In this example, the File object is created using the path of the text file.
- The Scanner object is then used to read the contents of the file line by line using a while loop.
- Each line is printed to the console using the println() method.
- Finally, the Scanner object is closed using the close() method.
- Log in to post comments