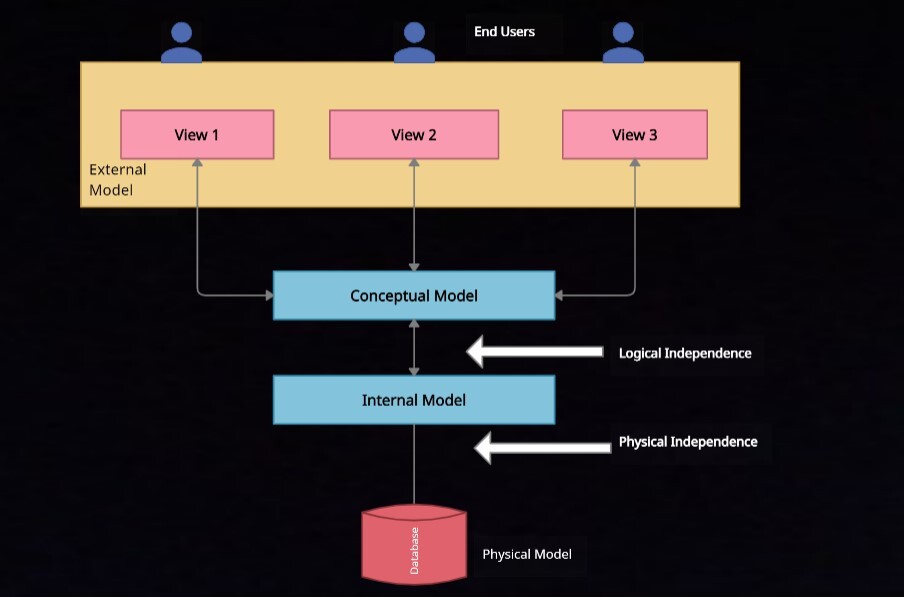
Internal Model Database
- The internal model represents a database in the perspective view of a database.
- This model depicts a database as a collection of fixed-size records meaning that the database holds a fixed size.
- It can be pretty close to the physical layer/ File structure.
- It is the exact representation of the database.
- It asks the designer to match it up to that of the conceptual model's characteristics and constraints.
- Maps the conceptual model entities to the table present in the relational model.
External Data Model
- The external model gives the user endpoint of view of the database.
- When seen closer, this resembles the real-world scenario, or we can say related to that when observed by each user.
- There may be a constraint within a database about certain information it presents.
- For example, one user is not interested in the data of another users data.
- An HR dept data is not interested in seeing data based on sales.
- The external model subdivides the requirements and constraints that can be examined within their external model framework.
- This means it divides between Hr dept and sales.
These are some of the basic stuff we need to know about internal and external data models.
- Log in to post comments