With the cypress writeFile command, we can write to a file with the specified contents.
Syntax:
cy.writeFile(filePath, contents)
cy.writeFile(filePath, contents, encoding)
cy.writeFile(filePath, contents, options)
cy.writeFile(filePath, contents, encoding, options)Arguments Used In WriteFile:
filePath: Path to the file within the project root.
Contents: It can be a string, array, object, or even buffer.
Encoding: Encoding is followed while writing a file. This can be,
- 'ascii'
- 'base64'
- binary'
- 'hex'
- 'latin1'
- 'utf8'
- 'utf-8'
- 'ucs2'
- 'ucs-2'
- 'utf16le'
- 'utf-16le'
- null
Null allows us to write a buffer directly.
Options:
Log: Displays commands in the command log.
Flag: File system flag.
Encoding: utf8 is the default.
Timeout: Time to wait for .writeFile.
Write Data Into JSON:
- Using writeFile(), we can write data in a JSON file.
- We can also retrieve the data using readFile().
Example:
cy.writeFile("name.json", { "data" });Let us write some data into a JSON using writeFile().
cy.writeFile("NarutoBio.json",{name:"Naruto",clan:"Uzumaki",occupation:"Hokage"})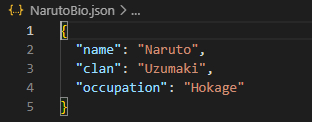
We can see it has created a JSON file with the name we specified in the project root.
Let us try to verify the file.
cy.readFile('D:/iVagus/Cypress/CYPRESS-TESTING-PROJECT/NarutoBio.json').then(Naru => {
expect(Naru.name).to.eq("Naruto")
expect(Naru.spouse).to.eq("Hinata")
cy.log(Naru.occupation)
})
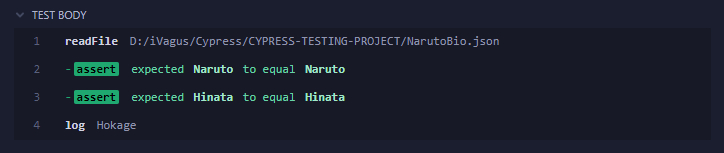
We can see that the file we wrote exists and can be verified using the readFile.
- Log in to post comments