Apache Hadoop HDFS Commands & Operations
HDFS Commands:
- hadoop fs -ls <path> list files in the path of the file system
- hadoop fs -chmod <arg> <file-or-dir> alters the permissions of a file where <arg> is the binary argument e.g. 777
- hadoop fs -chown <owner>:<group> <file-or-dir> change the owner of a file
- hadoop fs -mkdir <path> make a directory on the file system
- hadoop fs -put <local-origin> <destination> copy a file from the local storage onto file system
- hadoop fs -get <origin> <local-destination> copy a file to the local storage from the file system
- hadoop fs -copyFromLocal <local-origin> <destination> similar to the put command but the source is restricted to a local file reference
- hadoop fs -copyToLocal <origin> <local-destination> similar to the get command but the destination is restricted to a local file reference
- hadoop fs -touchz create an empty file on the file system
- hadoop fs -cat <file> copy files to stdout
- yarn node -list list nodes in the yarn cluster
- yarn node -status <node id> status of a node (memory used, free, number of containers, etc) for <node id> (first column from command above)
- yarn application -list list of Yarn applications and their state
- yarn logs -applicationId <appid> dump the logs for a particular application
- hdfs getconf return various configuration settings in effect
- hdfs getconf -namenodes namenodes in the cluster
- hdfs getconf -confkey <a.value> return the value of a particular setting (e.g. dfs.replication)
- hdfs dfsadmin -safemode get find out if you’re in safemode
- hdfs dfsadmin -report find out how much disk space us used, free, under-replicated, etc.
- kodoop sql <cluster> run an SQL session against the running server. <user> defaults to sys.
- kodoop server <cluster> start start the server, incorporating any new config file changes. Memory images will persist. If the server is currently running, this command restarts it.
- kodoop server <cluster> stop stop the server. Memory images will persist so long as the cluster remains active.
- kodoop server <cluster> status show the status of the server.
- kodoop cluster <cluster> initialize initialize the server. Erase existing data/metadata.
- kodoop cluster <cluster> stop stop the cluster’s YARN application. This will shut down everything except the edge nodes. Memory images will be lost but internal data will persist in HDFS.
- kodoop cluster <cluster> restart stop and then start again.
- kodoop mgr <cluster> shell run a sub-shell configured to allow users to directly run the management commands from the WX2 software.
- kodoop help find out about Kognitio on Hadoop commands
- kodoop testenv check Kognitio on Hadoop environment is configured correctly
- kodoop list_clusters show the currently configured Kognitio on Hadoop clusters
- kodoop server <cluster> diagnose check for problems with a server
- kodoop server <cluster> [auto|manual] turn automatic management on or off (defaults to on)
- kodoop server <cluster> viconf change server config settings
- kodoop incidents <cluster> list list of incidents (container failures, etc) the cluster has recovered from
- kodoop gateway <cluster> restart restart a hung gateway (was an issue for older versions)
- kodoop sql <cluster> quick SQL connection to the cluster as the sys user
HDFS Operation
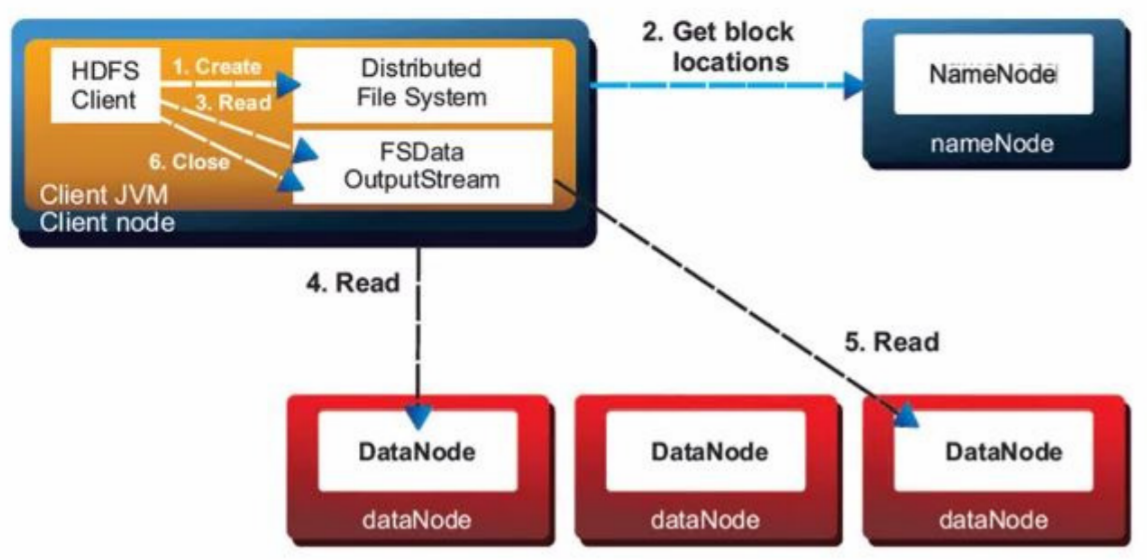
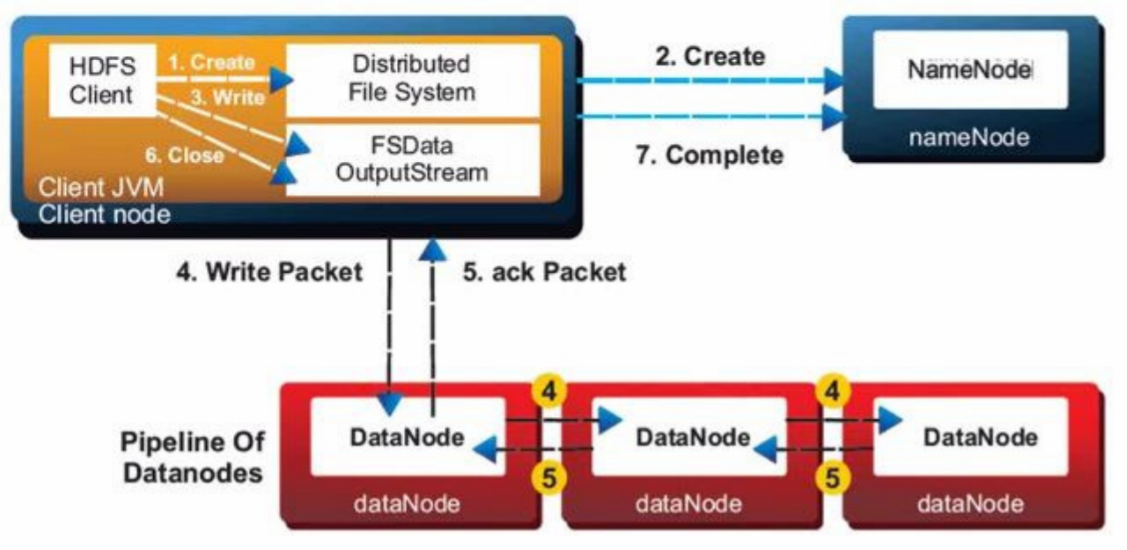
- Client makes a Write request to Name Node
- Name Node responds with the information about on available data nodes and where data to be written.
- Client write the data to the addressed Data Node.
- Replicas for all blocks are automatically created by Data Pipeline.
- If Write fails, Data Node will notify the Client and get new location to write.
- If Write Completed Successfully, Acknowledgement is given to Client
- Non-Posted Write by Hadoop
HDFS: File Write
HDFS: File Read